3-Phase Induction Motor
Also Read
☞ DC Motor
☞ Also learn type of motor
☞ induction motor visit
☞ Electrical Machine visit
☞ Amazing knowledge about Transformer
☞ Step down and step up transformer
☞ Dc Generator working visit
☞ knowledge about DC Motor
☞ Amazing knowledge about Transformer
☞ Step down and step up transformer
☞ Dc Generator working visit
☞ knowledge about DC Motor
Introduction of induction motor :
We know without electrical machine any industry is not work, specially without transformer and motor
Induction motor is invented by great scientist 'Nikola Tesla' this is most common motor type. It consume almost 50% of overall power consumption in the world.
Induction machines are also called asynchronous machines i.e., the Electrical Machine which never run at a synchronous speed. Whenever we say induction machine we mean to say induction motor. Induction motors may be single-phase or three-phase. The single phase induction motors are usually built in small sizes (upto 3 H.P). Three phase induction motors are the most commonly used AC motors in the industry because they have simple and rugged construction, low cost, high efficiency, reasonably good power factor, self-starting and low maintenance cost. Almost more than 90% of the mechanical power used in industry is provided by three phase induction motors. That's why it is also called horse of industry.
☞ Step up & down transformer visit
Principle of induction motor
There are may types of motor available but induction motor is most use full in all type of industry.
"3-phase induction motor generally works on principle of electromagnetic induction."
Construction of induction motor :
A 3-phase induction motor consists of two main parts, namely stator and rotor.
☞ learn type of transformer visit
(1) Stator :
It is the stationary part of the induction motor. It has three main parts, namely.
(i) Outer frame,
(ii) Stator core and
(iii) Stator winding
(i) Outer frame: It is the outer body of the induction motor. Its function is to support the stator core and to protect the inner parts of the machine. For small machines the frame is casted but for large machines it is fabricated. To place the motor on the foundation, feet are provided in the outer frame as shown in Fig. (a)
☞ knowledge about DC Motor visit
(ii) Stator core: When AC supply is given to the induction motor, an alternating flux is set -up in the stator core. This alternating field produces hysteresis and eddy current loss. To minimise these losses, the core is made of high grade silicon steel stampings. The stampings are assembled under hydraulic pressure and are keyed to the frame. Each stamping is insulated from the other with a thin varnish layer. The thickness to the stamping usually varies from 0.3 to 0.5 mm. Slots are punched on the inner periphery of the stampings, as shown in Fig.(b) to accommodate stator winding.
☞ knowledge about DC Motor visit
(iii) Stator winding : The stator core of induction motor carries a three phase winding which is usually supplied from a three phase supply system. The six terminals of the winding (two of each phase) are connected in the terminal box of the machine. The stator of the motor is wound for definite.number of poles, the exact number being determined by the requirement of speed. It will be seen that greater the number of poles, the lower is the speed and vice-versa.
(2) Rotor :
The rotating part of the induction motor is called rotor. Two types of rotors are used for 3-phase induction motors.
(i) Squirrel cage rotor
(ii) Phase wound rotor
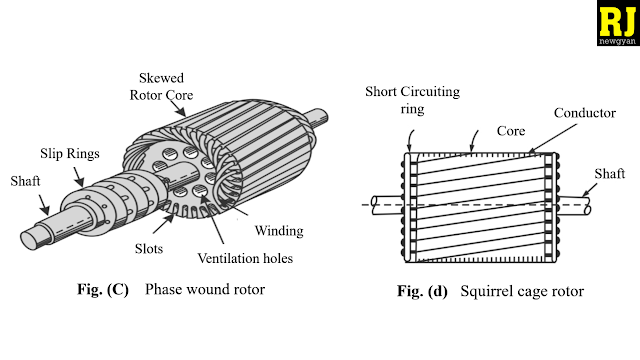
(i) Squirrel cage rotor : The induction motors in which these rotors are employed are called Squirrel cage induction motors. Because of simple and rugged construction, the most of the induction motors employed in the industry are of this type. A squirrel cage rotor consists of a laminated cylindrical core having semi-closed circular slots at the outer periphery. Copper or aluminium bar conductors are placed in these slots and short circuited at each end by copper or aluminium rings, called short circuiting rings, as shown in Fig. (d). Thus, in these rotors, the rotor winding is permanently short-circuited and no external resistance can be added in the rotor circuit. Figure (d) clearly show that the slots are not parallel to the shaft but these are skewed. The skewing provides the following advantages:
(a) Humming is reduced, that ensures quiet running.
(b) At different positions of the rotor, smooth and sufficient torque is obtained.
(c) It reduces the magnetic locking of the stator and rotor,
(d) It increases the rotor resistance due to the increased length of the rotor bar conductors.
(ii) Phase wound rotor : It is also known as slip ring rotor and the motors in which these rotors are employed are known as phase wound or slipring induction motors. This rotor is also cylindrical in shape which consists of large number of stampings. A number of semi-closed slots are punched at its outer periphery. A 3-phase insulated winding is placed in these slots. The rotor is wound for the same number of poles as that of stator. The rotor winding is connected in star and its remaining three terminals are connected to the slip rings. The rotor core is keyed to the shaft. Similarly, slip-rings are also keyed to the shaft but these are insulated from the shaft. (see Fig. (c) ). In this case, depending upon the requirement any external resistance can be added in the rotor circuit. In this case also the rotor is skewed. A steel shaft is passed through the centre of the rotor and is fixed to it with key. The purpose of shaft is to transfer mechanical power.
Working of induction motor :
When 3-phase supply is given to the stator winding of a 3-phase wound induction motor, a revolving field is set up in the stator core. The resultant magnetic field set-up by the stator core, at any instant. As per the supply sequence, this field is rotating in an anti-clockwise direction at synchronous speed Zs radian per second. The revolving field is cut by the stationary rotor conductors and an emf is induced in the rotor conductors. Since the rotor conductors are short circuited, current flows through them. A resultant field (Fr) is set-up by the rotor current carrying conductors. This field tries to come in line with the stator revolving field (Fm), due to which an electromagnetic torque (Te) develops and rotor starts rotating in same direction as that of stator revolving field.
Application of induction motor :
- Use where high starting torque and low starting current.
- Use where speed control is require.
- It is cranes, pumps, elevators and compressors.
Other :
Important equation :
- Synchronous speed, Ns = 120f / P
- Fractional speed, S = (Ns - N) / Ns
- Percentage slip, %S = [(Ns - N) / Ns]*100
- Rotor speed, N = Ns (1 - S)
1-Phase Induction Motor
Introduction :
A single-phase induction motor is very similar to a 3-phase squirrel cage induction motor in construction. The pictorial disassembled view of a single phase induction motor is shown in Fig. 11.1.
Similar to 3-phase induction motor it consists of two main parts namely stator and rotor.
Principle :
It's work on principle of induction motor.
"When current carrying conductor placed in magnetic field it experiences a rotating force
Also Read
☞ induction motor visit
☞ Electrical Machine visit
☞ Amazing knowledge about Transformer
☞ Step down and step up transformer
☞ Dc Generator working visit
☞ knowledge about DC Motor
☞ Amazing knowledge about Transformer
☞ Step down and step up transformer
☞ Dc Generator working visit
☞ knowledge about DC Motor
☞ 25 amazing facts about Electrical
☞ Electrical Machine
☞ Transformer
☞ Step down and step up transformer
☞ DC Generator
☞ DC Motor
☞ What is insulation co-ordination ?
☞ Electrical Full forms
☞ Corona update ?
☞ English Sentence formation
☞ What is Facebook ?
☞ Electrical Machine
☞ Transformer
☞ Step down and step up transformer
☞ DC Generator
☞ DC Motor
☞ What is insulation co-ordination ?
☞ Electrical Full forms
☞ Corona update ?
☞ English Sentence formation
☞ What is Facebook ?


إرسال تعليق