☞ Home visit
☞ Synchronous machine visit
☞ Step up & down transformer visit
☞ Transformer visit
☞ DC Motor visit
☞ Synchronous machine visit
Transformer is a machine which is use to step up and step down (increase & reduce) voltage level without change in frequency.
Acording to function it is classified as a Step up & step down transformer.
Transformer consists a two winding which is wounded on magnetic core, a winding which connects with a.c supply is called primary winding and a winding which connects with load is called secondary winding.
Loss in transformer is completely depend on it's windings and magnetic core.
There are generally two types of losses acure in transformer during operation.
(1) Iron loss (core loss)
(2) Couper loss
(1) Iron loss : loss which occurs due to magnetic core (which made of iron) is called iron loss or core loss.
There are two types of iron loss
(a) Hysteresis loss
(b) Eddy current loss
These both loss is mainly depend on frequency
☞ Step up & down transformer visit
(a) Hysteresis loss : This type of loss occurs due to the hysteresis effect. when alternating current pass through primary winding core get magnetized. So at every cycle energy loss proportional to the area of the hysteresis loop occurs.
This loss is proportional to the frequency of the a.c supply & it's denoted by Wₕ.
Wₕ= η (Bₘ)^1.6 f V
Where
η = Steinmetz constant j/m³
Bₘ = Maximum flux density Wb/m²
f = Frequency Hz
V = volume of core m³
Generaly the value of η & volume are constant so Wₕ= (Bₘ)^1.6
If Bₘ is constant, hysteresis loss directly proportional to the supply frequency (f).
Wₕ∝ f
If the value of Bm and f both remain constant, hysteresis loss remain constant.
☞ Synchronous machine visit
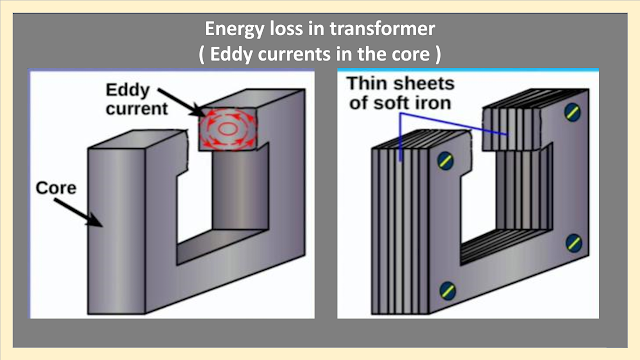
(b) Eddy current loss : During operation alternating magnetic field is produced due to alternating a.c supply. Due to this alternating field emf is induced and eddy current are produced in the core.
Power loss occurs in the core due to internal resistance of core and the eddy currents. This loss is called eddy current loss.
Wₑ = P (Bₘ)² f² t²
Where
P = Constant
Bₘ = Maximum flux density Wb/m²
f = Frequency Hz
t = Thickness of lamination (m)
For particular transformer the value of 't' is constant.
If 'Bₘ' is constant, the eddy current loss directly proportional to the square of frequency.
Wₕ∝ f²
(2) Copper loss : This loss acure due to voltage drop in transformer windings. When a.c supply is given to primary of transformer the current flow in both winding. Due to winding resistance I²R (copper) loss produce. It is denoted by Wc
Wc = I²R
Where
R = Resistance of windings
I = Current through windings
If R is constant, this loss is directly proportional to squre of current.
Total loss in transformer is given by
Wₜ = Wₕ + Wₑ + Wc
Where :
Wₜ = total loss
Wₕ = hysteresis loss
Wₑ = eddy current loss
Wc = copper loss
☞ Electrical full form visit


إرسال تعليق